氫氣的生物學效應發現以來,已經有大量動物和臨床研究證明這種簡單的氣體可以作為預防和治療疾病的潛在手段,由於氫具有極大的生物安全性,使這種療法具有極大而廣泛的應用價值,作為一種治療手段,對胎兒是否具有危害是非常重要的問題,因此研究相關問題也十分重要,雖然目前仍沒有針對胎兒安全性的研究,但這類研究也同樣具有借鑒的價值,因為可以緩解一些能引起胎兒傷害的因素導致的損傷,這給這一方法的長期安全性增加了部分證據。
為什麼要開展這類研究,作者的看法是:胎兒在子宮內和出生時發生腦缺血缺氧是導致急性新生兒死亡和長期大腦功能障礙的重要原因。有些新生兒腦損傷如中風,在新生兒中可以高達1/4000。95%的這些患兒可以生活到成年,但這些患者往往遺留部分運動和認知功能障礙,這些不同形式的新生兒腦損傷對這些患者本人、家庭和社會帶來巨大的經濟負擔。因此,尋找可以預防胎兒和新生兒腦損傷的方法顯得尤其重要和迫切。(前言中的規法寫法,背景介紹部分,也就是針對這個疾病研究的必要性)
日本學者最近研究發現,給懷孕大鼠喝氫水,可以保護因為子宮缺血導致的胎兒腦缺血損傷,避免出生動物成年後學習記憶能力下降,提示氫水可能有保胎的作用。中國學者曾經用妊娠高血壓動物模型證明,注射氫氣鹽水可以使動物出生的後代體重和存活率增加,這一最新研究是針對一過性子宮缺血引起的後代腦損傷。兩者研究的疾病類型不同,一是急性損傷,一個是慢性傷害,但都確定氫氣可以保護胎兒在子宮內的傷害,提示氫氣可能作為保胎手段。
氫水的製備方法可透過1.電解,2.水與礦石反應、3.高壓灌注,選擇任一方法均可備製水中含氫之氫水,任一方法皆可並無特殊性、惟成本與時間之差異。日本、韓國、中國研究中使用之氫水,均因其實驗設計使用三種方式產生氫水,水中含氫氣即為氫水,檢測方法須應用溶氫檢測儀檢測之、只要水中含氫氣即為醫學研究所定義之氫水。
最新研究發表在《自由基生物醫學》雜誌,也是氫氣生物學領域在這個雜誌上發表的第2篇論著,第一篇是我們課題組去年發表的用誘導腸道細菌產生氫氣治療大鼠腦缺血的工作。這一新的研究論文的責任作者是Shinya Toyokuni教授,Toyokuni是名古屋大學大學院醫學院病理學和分子病理診斷學講座教授,長期從事各類氧化應激相關疾病的研究,涉及的領域主要是腫瘤和中樞神經系統損傷等。後面有他的相關資訊,在投稿論文時,可以作為推薦審稿專家資訊,供大家參考。
研究摘要图
Shinya Toyokuni, M.D./Ph.D.

Professor,Department of Pathology and Biological Responses
NagoyaUniversity Graduate School of Medicine
65Tsurumai-cho, Showa-ku, Nagoya 466-8550, Japan
Tel:+81-52-744-2086;Fax: +81-52-744-2091
Skype:Shinya.Toyokuni
ResearcherID:http://www.researcherid.com/rid/C-1358-2010
SFRRAsia Representative
Executiveeditor: J Clin Biochem Nutr
Associateeditor: Arch Biochem Biophys, Cancer Sci, Free Radic Res and Pathol Int
Editorin chief: Nagoya J Med Sci; http://www.med.nagoya-u.ac.jp/medlib/nagoya_j_med_sci/7312/7312.html
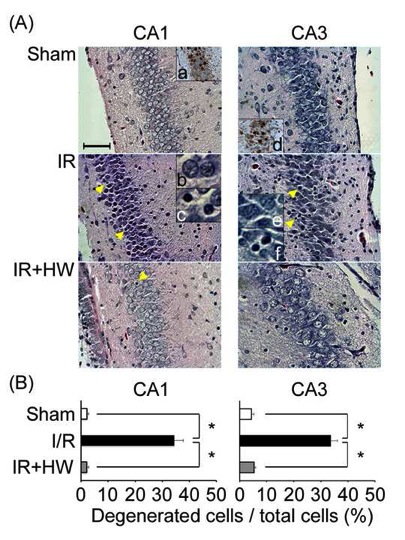
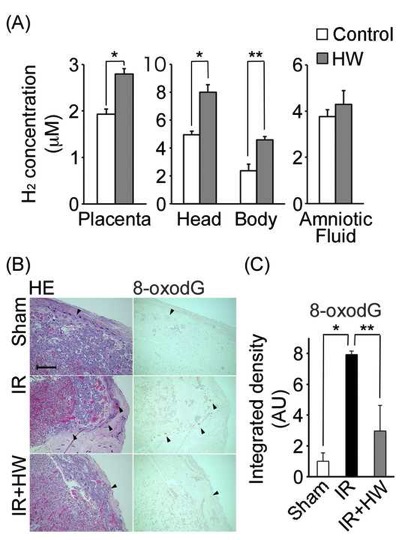
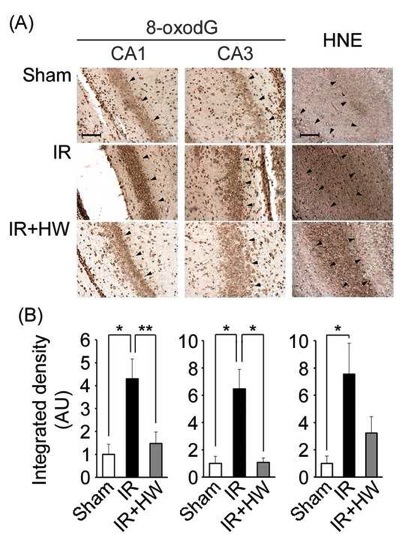
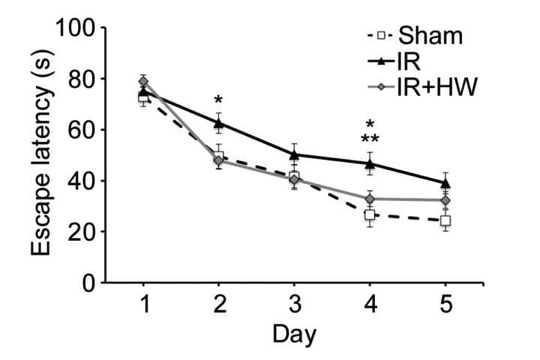
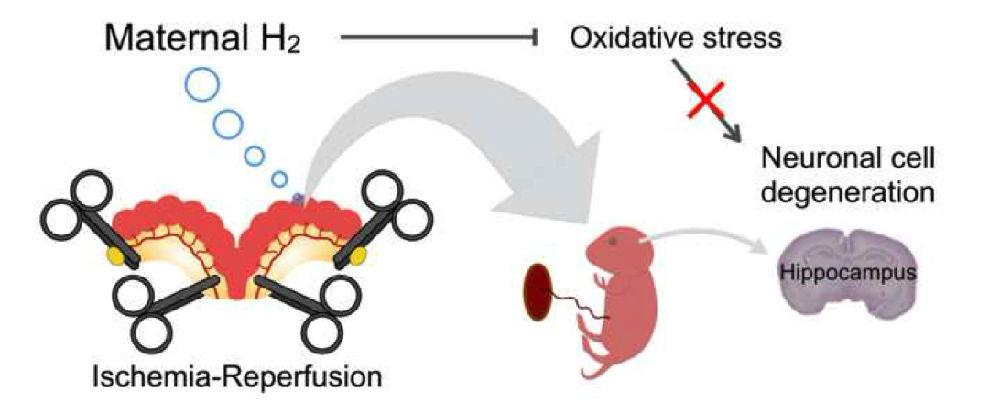
Molecular hydrogen(H2) scavenges hydroxyl radicals. Recently, H2 has beenreported to prevent a variety of diseases associated with oxidative stress inmodel systems and in humans. Here, we studied the effects of H2 onrat fetal hippocampal damage by ischemia and reperfusion (IR) on day 16 ofpregnancy with the transient occlusion of the bilateral utero-ovarian arteries.Starting 2 days prior to the operation, we provided the mothers withhydrogen-saturated water ad libitum until vaginal delivery. We observeda significant increase in the concentration of H2 in the placentaafter the oral administration of hydrogen-saturated water to the mothers, withless placental oxidative damage after IR in the presence of H2.Neonatal growth retardation was observed in the IR group, which was alleviatedby the H2 administration. We analyzed the neuronal cell damage inthe CA1 and CA3 areas of the hippocampus at day 7 after birth byimmunohistochemical analysis of the 8-oxo-7,8-dihydro-2'-deoxyguanosine and4-hydroxy-2-nonenal-modified proteins. Both oxidative stress markers weresignificantly increased in the IR group, which was again ameliorated by the H2intake. Lastly, 8-week-old rats were subjected to a Morris water maze test.Maternal H2 administration improved the reference memory of theoffspring to the sham level after IR injury during pregnancy. Overall, thepresent results support the idea that maternal H2 intake helpsprevent the hippocampal impairment of offspring induced by IR during pregnancy.

沒有留言:
張貼留言
您好 歡迎至FB網頁留言討論
本處以庫存文章為主
討論請至FB能有較即時的交流與互動